Message Offload¶
1. Background: Why Message Offload?¶
The Agent Context Challenge¶
In modern AI agent systems, LLMs interact with tools through iterative loops, accumulating conversation history and tool results. With each iteration, a critical problem emerges:
The Core Problem: Context Window Explosion
When an agent executes complex tasks, it relies on maintaining conversation history to track progress and make informed decisions. However:
Rapid Context Growth: Each tool call appends input parameters and output results to message history
Token Consumption: A single tool call can consume hundreds or thousands of tokens, especially for data-heavy operations
Context Window Limits: Most LLMs have finite context windows (e.g., 128K, 200K tokens)
Context Rot: As context grows beyond optimal thresholds, model performance degrades significantly
Example: Web Research Agent
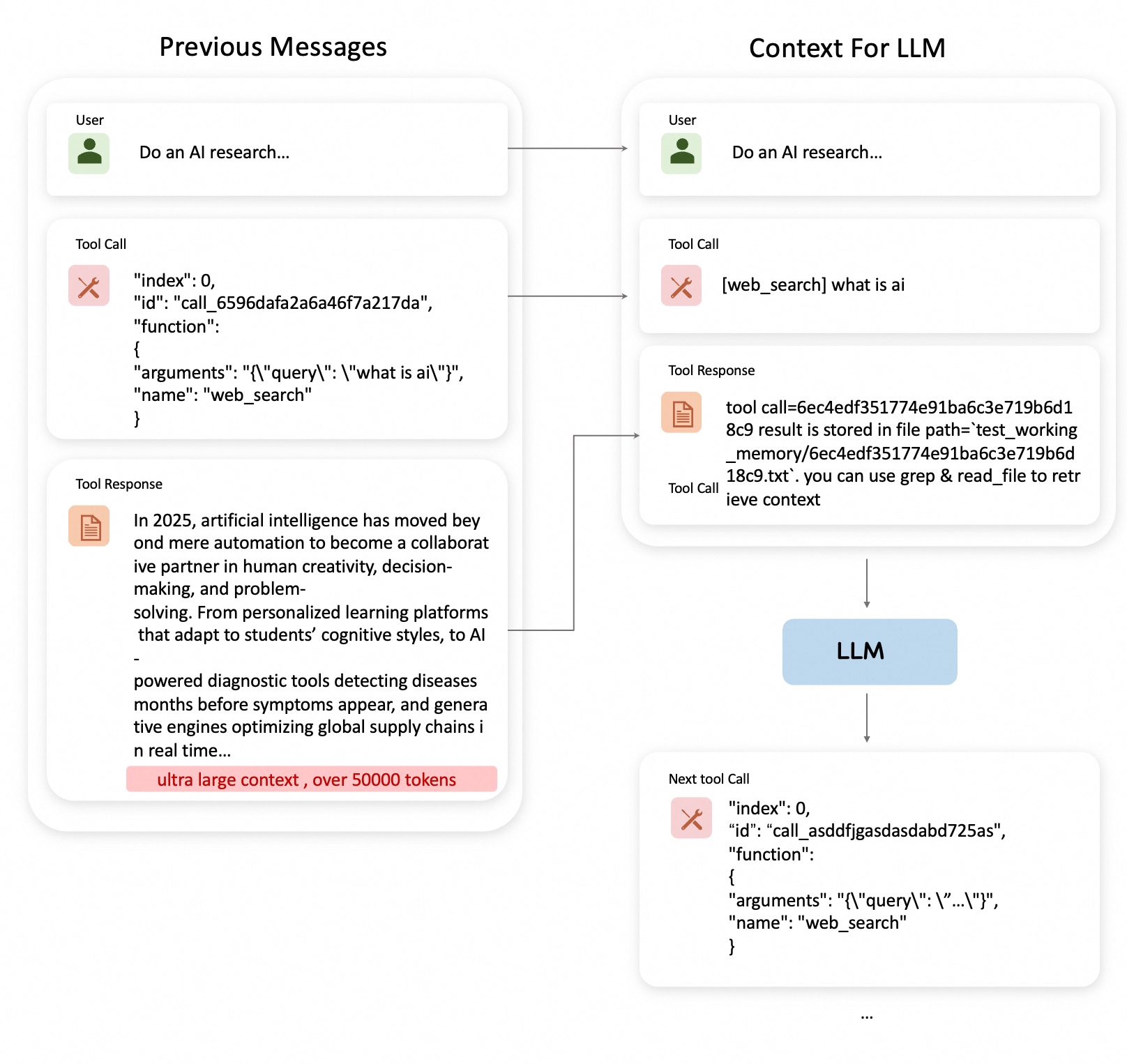
Imagine an agent performing research across multiple sources:
Iteration 1: web_search("AI context management") → 3,500 tokens
Iteration 2: read_webpage(url_1) → 8,200 tokens
Iteration 3: web_search("context compression techniques") → 4,100 tokens
Iteration 4: read_webpage(url_2) → 7,800 tokens
...
Iteration 15: summarize_findings() → Total context: 95,000 tokens
As context accumulates:
At 50K tokens: Agent performs normally, accurate responses
At 100K tokens: Responses become repetitive, slower inference
At 150K tokens: Significant quality degradation, “context rot” sets in
At 200K tokens: Context window exhausted, cannot continue
Without context management, agents hit walls after just 15-20 complex tool calls.
The Solution: Message Offload as Context Engineering¶
Message Offload solves this by intelligently moving non-essential information out of active context, allowing agents to operate indefinitely while maintaining optimal performance:
1. Message Compaction (Reversible Strategy)
Selective Storage: Large tool results stored in external files
Reference Retention: Only file paths kept in message history
On-Demand Retrieval: Full content can be retrieved when needed
2. Message Compression (LLM-Based Strategy)
Intelligent Summarization: LLM generates concise summaries of older message groups
Priority Preservation: Recent messages and system prompts remain intact
Information Density: Maintains key information while reducing token count
3. Hybrid Auto Mode (Adaptive Strategy)
Compaction First: Applies compaction to tool messages
Compression When Needed: Triggers compression if compaction ratio exceeds threshold
Dynamic Adjustment: Adapts strategy based on context characteristics
Enhanced work memory management¶
Instead of letting context grow uncontrollably, the agent now benefits from:
Traditional Approach (No Context Management):
50 messages → 95,000 tokens → Context rot begins
- Response quality: Degraded
- Inference speed: Slow
- Can continue: No (approaching limit)
- Information lost: No, but unusable
+ Message Offload Approach:
50 messages → 15,000 tokens (after offload) → Optimal performance maintained
- Response quality: High
- Inference speed: Fast
- Can continue: Yes (85% headroom remaining)
- Information lost: No (stored externally, retrievable)
Offload Details:
- 20 tool messages compacted → Stored in /context_store/
- 15 older messages compressed → Summarized in system message
- 5 recent messages preserved → Full content intact
- External storage: 80,000 tokens offloaded
- Active context: 15,000 tokens (84% reduction)
This managed context enables the agent to:
Operate Indefinitely: No hard limit on conversation length
Maintain Performance: Stay within optimal token range (10-30K tokens)
Preserve Information: All data accessible through file system or summaries
Optimize Costs: Reduce token consumption by 70-90% in long conversations
The Impact: From Context Explosion to Controlled Growth¶
Traditional Approach (No Work Memory Management):
Agent: "I've executed 20 tool calls, context is now 100K tokens"
→ Performance degradation begins
→ Slower responses, repetitive outputs
→ Cannot continue beyond 30 calls
→ Task abandoned due to context limits
Message Offload Approach (Intelligent Management):
Agent: "I've executed 100 tool calls, active context maintained at 18K tokens"
→ Optimal performance throughout
→ Fast, accurate responses
→ Can continue indefinitely
→ All historical data accessible when needed
Real-World Impact:
Before Message Offload (20 tool calls):
- Active context: 95,000 tokens
- Performance: Degraded (context rot)
- Can continue: No (near limit)
- Response quality: 6/10
- Inference time: 8-12 seconds
- Max task complexity: Low (15-20 calls)
After Message Offload (100 tool calls):
- Active context: 18,000 tokens (-81%)
- Performance: Optimal
- Can continue: Yes (90% headroom)
- Response quality: 9/10
- Inference time: 2-4 seconds (-70%)
- Max task complexity: High (100+ calls)
2. Implementation in ReMe¶
ReMe has fully implemented the above-mentioned message offload and reload mechanisms, inspired by Context Engineering for AI Agents with LangChain and Manus. The implementation provides two core operation primitives:
(1) Message Offload Operations¶
Operations for intelligently reducing context size through compaction and compression strategies.
📖 Detailed Usage Guide: Message Offload Ops
Key features:
Three working summary modes: compact, compress, and auto
Intelligent token threshold management
Integration with file storage system
Complete working examples in test files
(2) Message Reload Operations¶
Operations for retrieving and accessing offloaded content when needed.
📖 Detailed Usage Guide: Message Reload Ops
Key features:
Text search within offloaded files (GrepOp)
Efficient file reading with pagination (ReadFileOp)
Support for both absolute and relative paths
Complete working examples in test files
Both operation primitives are production-ready and can be integrated into your agent workflows. Refer to the linked documentation for API specifications, parameter details, and practical usage examples.
3. Integrating Working Memory with Agents¶
ReMe provides a complete tutorial on integrating working memory mechanisms with agent workflows. This integration enables agents to handle long-running tasks efficiently while maintaining optimal context window usage.
Resources¶
📖 Tutorial Guide: Working Memory Quick Start
Step-by-step guide on integrating working memory with agents
Configuration examples and best practices
Real-world usage scenarios
💻 Implementation Reference: react_agent_with_working_memory.py
Complete implementation of a ReAct agent with working memory
Shows how to configure message offload and reload operations
Production-ready code template
🚀 Demo Application: work_memory_demo.py
Runnable demonstration of working memory in action
Practical examples with different scenarios
Easy to adapt for your own use cases
These resources provide everything you need to add intelligent working memory management to your agent applications.